StarHorse on PUNCH4NFDI Infrastructure
First production run successful
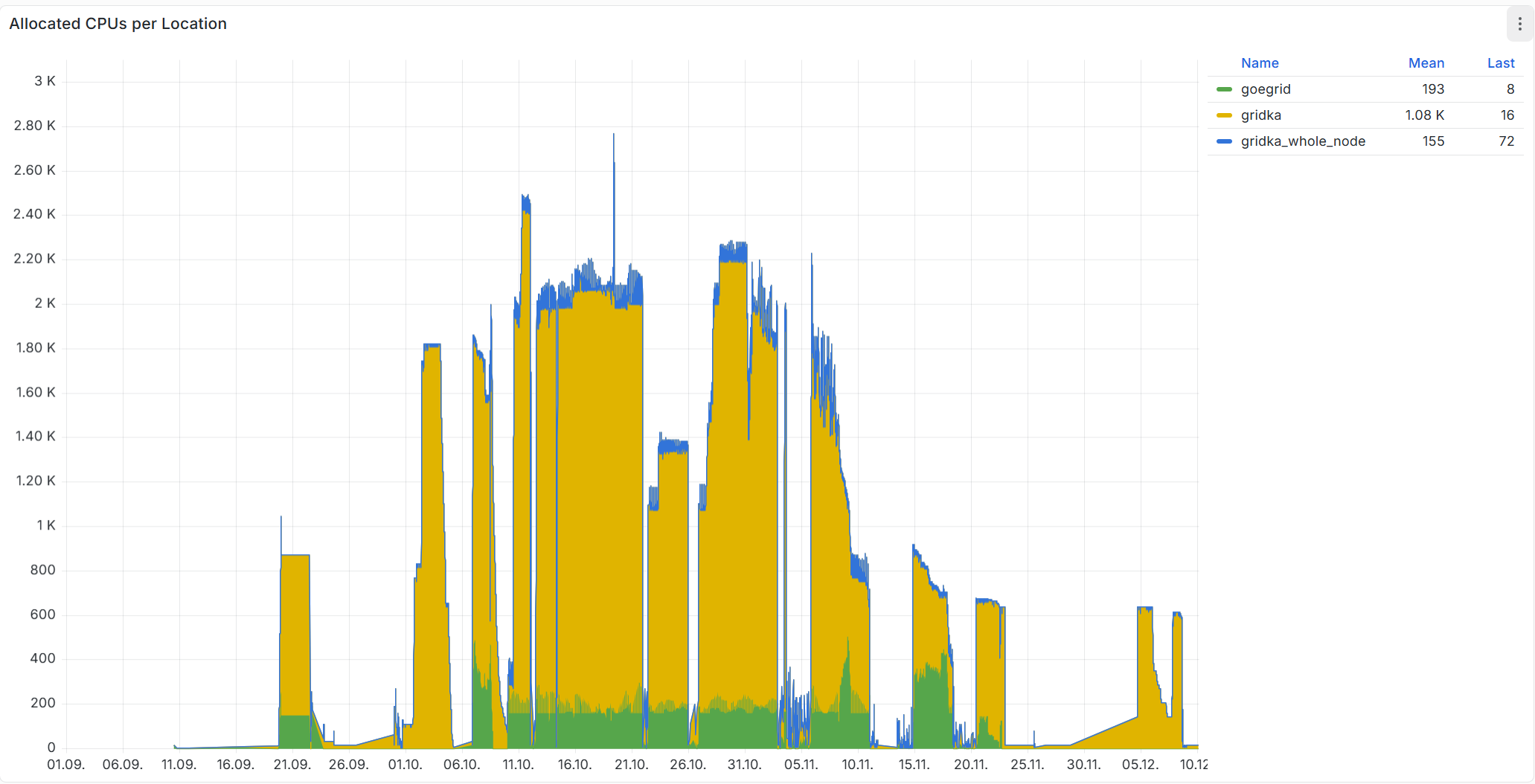
Number of cores allocated on Compute4PUNCH during the StarHorse run.
In the last weeks of 2025, the Annual Meeting[1] of the PUNCH4NFDI Consortium took place (19 and 20 November at the AIP, Potsdam), celebrating an important milestone for the project: the successful completion of the first production run of the StarHorse analysis framework on the PUNCH4NFDI federated infrastructure. Presented[2] by Arman Khalatyan (StarHorse team, AIP) and Elena Sacchi (PUNCH4NFDI team, AIP), this achievement demonstrates the operational readiness of the consortium's computing resources and workflow integration systems[3].
The Achievement
The three-week production run utilised over 2,000 CPU cores (see the figure at top) to conduct large-scale stellar analysis on the PUNCH4NFDI infrastructure. Approximately 500,000 CPU hours were consumed to calculate stellar parameters using the StarHorse code[4], demonstrating substantial computational demand. The workflow was orchestrated using the REANA workflow engine[5] with the Compute4PUNCH backend, showcasing successful integration of multiple technical components (authentication, job orchestration, computing and storage resources, execution) across the federated infrastructure. This test validated the ability of PUNCH4NFDI to support production-grade scientific analyses at substantial computational scale.
Technical Components and Infrastructure
The success of this run was built on two critical infrastructure elements:
Compute4PUNCH (C4P): provides a federated computing environment integrating heterogeneous resources from consortium partner institutions (DESY, KIT, LMU, LRZ, Münster). Drawing on proven technologies from the Large Hadron Collider computing grid (WLCG), Compute4PUNCH (C4P) manages approximately 2,000 cores and provides dynamic resource allocation for distributed workflows.
REANA: a workflow execution engine that captures complete analysis environments—including software dependencies, input data, and computational steps—ensuring reproducibility and portability across systems. REANA hosted by AIP, specifically for PUNCH4NFDI use cases and the PUNCH community, supports both batch processing and interactive analysis through specialised applications (e.g., JupyterLab, VS Code).
Key Collaborators
The successful integration of StarHorse with PUNCH4NFDI infrastructure relied on close collaboration between multiple institutions. The AIP team, combining StarHorse expertise and PUNCH4NFDI coordination , provided domain knowledge and scientific requirements. The computing infrastructure team from KIT Scientific Computing Center (SCC) contributed expertise in federated computing and resource management to establish C4P as a reliable backend. The collaboration with Tibor Šimko (CERN), lead developer of REANA, was instrumental in adapting and extending REANA to support the C4P backend, enabling rapid deployment of StarHorse on PUNCH4NFDI infrastructure.
About StarHorse
StarHorse is a Bayesian isochrone-fitting code developed at AIP for deriving fundamental stellar parameters including distances, extinctions, and ages. The framework processes data from the Gaia space mission combined with spectroscopic surveys (GALAH, LAMOST, APOGEE, RAVE, SDSS, and Gaia-ESO), enabling comprehensive studies of Milky Way structure and galactic archaeology (see the figure below). The successful production run on PUNCH4NFDI infrastructure opens new possibilities for researchers using StarHorse, whose data will be published on https://data.aip.de/, to conduct large-scale stellar population analyses.
Going Forward
This production run provides concrete evidence of PUNCH4NFDI's capability to support research workflows across the consortium's diverse scientific communities. As the consortium prepares for the second funding phase, experiences gained from the StarHorse run will provide further optimisation of the federated infrastructure, and increased usability of the services. The integration of C4P and REANA represents a model for sustainable, reproducible research analysis that other use cases can now adopt within PUNCH4NFDI and beyond.
References
-
PUNCH4NFDI Annual Meeting 2025. https://www.punch4nfdi.de/news_amp_events/news/archiv/annual_meeting_2025/
-
Khalatyan, A. (2025). StarHorse on REANA—General Meeting 2025. Presentation at PUNCH4NFDI Annual Meeting, Potsdam. https://indico.desy.de/event/48557/contributions/195405/attachments/100606/139601/Starhorse-REANA-GM2025-AIP-A.Khalatyan.pdf
-
PUNCH4NFDI Consortium. (2021). PUNCH4NFDI: Particles, Universe, NuClei and Hadrons for the NFDI. Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY. https://www.dfg.de/resource/blob/344878/punch4nfdi.pdf
-
Queiroz, A. B. A., Anders, F., Chiappini, C., et al. (2023). StarHorse results for spectroscopic surveys with Gaia EDR3. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 658, A56. https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202245399
-
REproducible ANAlysis (REANA) workflow engine. https://reana.io/